Theme 3 Health, Nutrition and Water Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
Background:
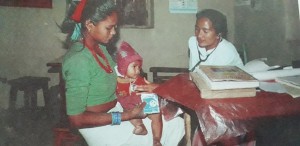
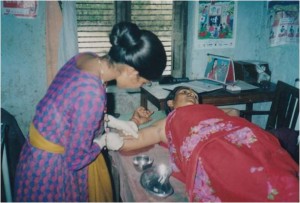
Socio-economic and , political changes and growth of population have affected health and nutrition positions in Nepal. There exists a 5% of child mortality rate in the world due to malnutrition. Malnutrition affects the physical, mental, and emotional development of children which in turn has a negative impact on a country’s social, economic, and human resource development. 36% (stunted ) short-heightened, 10% (Wasted )malnourished, 27% underweight (as per their age), and 53% of anemic children are reported amongst children below 5 years of age in Nepal. 17% ( Body Mass Index is <18.5) underweight and 41% anemic women of reproductive age have also been reported in Nepal (NDHS 2016). There are many other health issues seen in Nepal. 260,000 people are infected by Hepatitis A & B virus. Japanese encephalitis and other fatal deseases and viruses are common to human life. Sickle cell anemia now has become another complex epidemic in the Tharu communities.
BASE analysed HMIS data 2076 from 20 districts of province no. 5 and Sudurpaschim province in the field of health and nutrition sector which shows that there are 117 imunization centers and 9 OTC on average per district (5 districts’ data was analyzed). Similarly, there are 169,196 pregnant women and 268,922 mothers (1000 days mother) of under 2 years old children from 20 districts. 67.30% of delivery cases happened in the hospital. The data shows that there is still insufficient OTC and 32.70% delivery cases are happened unsafe in 20 districts. The mortality rate of 20 districts is 44.85.
Constitution of Nepal has provided provision for water, sanitation and hygiene as fundamental rights in Article 30 (1) and Article 35 (4).) According to the provision, every citizen has the right to live in a clean and healthy environment and right of access to clean drinking water and sanitation. 10.8 million people in Nepal do not have access to improved sanitation,and 3.5 million do not have access to basic water services. 20% of govrnment schools lack improved water and sanitation facilities, with an additionl 19 % lacking separate tiolets for girls and boys and menstrual hygiene management facilities.(UNICEF 2018-2022) It means every citizen should have access to adequate, acceptable for drinking, physically accessible and economically reliable clean drinking water, sanitation, and a healthy environment. SDG 6 has set a goal to “ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all” by 2030 and SDG 3 has declared its objective as to “ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.” Therefore, BASE has developed “Health, Nutrition and WASH” strategy to support the SDGs 3 and 6.
Goal, Objective and Strategy:
Goal:
Create a healthy and prosperous society by establishing a common people’s access to nutrition, quality health, and sustainable WASH service.
Objectives:
By end of 2023,
- To support health service centers to increase the number of OTC and to treat 15,000 severely malnourished children through the outreach therapeutic center (OTC).
- To support 1000 days mothers and children to prepare nutritional food by using local resources and food grains.
- To increase access to 250,000 women and adolescent girls to information about menstrual hygiene management (MHM).
- To improve health and social conditions of 50,000 vulnerable people through better service delivery from the health facilities.
- To provide easy access to safe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene facilities for 200,000 people.
- To raise awareness and change behaviour on the WASH practices to 20,000 households and 9419 early grade reading/basic level community schools.
- To support 1000 early grade reading schools/basic level community schools to establish basic structures for safe drinking water and sanitation utilities.
Strategy:
- Mobilize FCHVs and Traditional leaders to conduct awareness campaigns and provide nutrition education to 1000 days mothers through the health mother groups in the participation of family members communities to take health and nutrition services.
- Advocacy for and mobilization of local resources to construct necessary physical infrastructures for quality health services in partnership and collaboration with local level government.
- Promote new practices of health and nutrition by conducting advocacy, behaviour change communication, and campaigns with all level government and development partners (private and public sector) to improve basic health services.
- Mobilize BASE target group members during the local level planning process to include WASH, nutrition and basic health facilities in program and policies of local, province and federal government .
- Conduct campaigns against traditional and customary practices, and superstitions on menstruation.
- Strengthen and enhance the institutional (BASE and water user committees) capacity in the health, nutrition, WASH sector, and support to prepare policy and plan for institutional governance.
- Increase the participation of women and socially excluded group/community in the decision making process regarding safe drinking water, sanitation, hygiene, and infrastructure development.
- Advocate for gender and disability friendly sanitation facilities in health care facilities , ECD and Schools.
- Scale up sanitation social movement and the total sanitation concept.